
An encompassing review of meta-analyses and systematic reviews of the effect of oats on all-cause mortality, cardiovascular risk, diabetes risk, body weight/adiposity and gut health
Key Topics Covered
Encompassing Review
Comprehensive search of systematic reviews and meta-analyses
Explored effect of oats on all-cause mortality, cardiovascular risk, diabetes risk, body weight/adiposity, and gut health

Change in liking following the reduction in sweetness level of carbonated beverages: A randomized controlled parallel trial
Key Topics Covered
Clinical Intervention Study
Randomized, double-blind, controlled, parallel design
Study aimed to investigate whether different methods of reducing sweetness coming from sugar or low-calorie sweeteners could change sweetness preference and perceived intensity in US and Mexican adults

Chia seeds (Salvia hispanica L.), incorporated into cookies, reduce postprandial glycaemic variability but have little or no effect on subjective appetite
Key Topics Covered
-
Clinical Intervention Study
-
A controlled feeding experiment using a randomized, double-blind, cross-over design
-
Study aimed to determine the lowest effective dose of chia seeds that can elicit satiety & glucose control as compared to the control
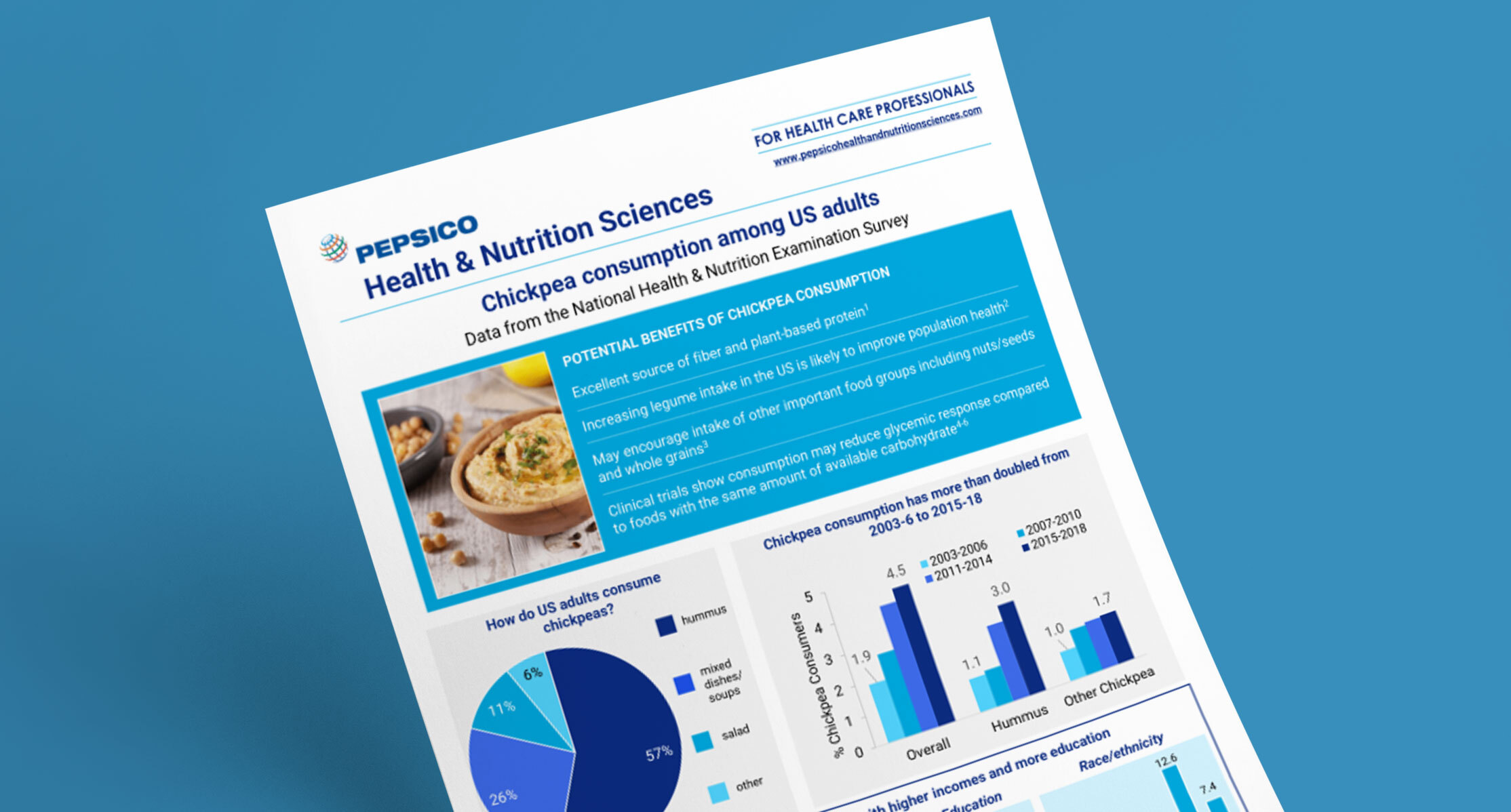
Trends and patterns of chickpea consumption among United States adults: Analyses of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data
Key Topics Covered
-
Epidemiology and Population Health Study
-
Data from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2003-2018
-
Explored trends and sociodemographic patterns among chickpea consumers

Estimated sweetness in US diet among children and adults declined from 2001 to 2018: A serial cross-sectional surveillance study using NHANES 2001–2018
Key Topics Covered
Epidemiology and Population Health Study
24-h dietary recall data of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES)
Evaluated trends in the sweetness (caloric or low-calorie sweetened) of the diet in US children and adults

Narrative review on the effects of oat and sprouted oat components on blood pressure
Key Topics Covered
-
Narrative Review
-
Comprehensive search of systemic reviews, meta-analyses, and clinical intervention studies
-
Explored oats and sprouted oat components and blood pressure

Oats lower age-related systemic chronic inflammation (iAge) in adults at risk for cardiovascular disease
Key Topics Covered
-
Clinical Intervention Study
-
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel arm design clinical trial
-
Researched the relationship between oats and systematic chronic inflammation

The inhibition of intestinal glucose absorption by oat-derived avenanthramides
Key Topics Covered
In Vitro Study
Cell models used to investigate the effect of the oat derived phenolic, avenanthramide, on intestinal glucose transporters
Tested the relationship between glucose uptake and the presence of avenanthramides

The importance of molecular weight in determining the minimum dose of oat β-glucan required to reduce the glycemic response in healthy subjects without diabetes: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis
Key Topics Covered
-
Systematic Review/Meta-Analysis
-
Linear associations assessed by random effect meta-regressions
-
Aimed to determine minimum amount of β-glucan required to reduce glycemic response

Balanced hybrid nutrient density score compared to Nutri-Score and Health Star Rating using receiver operating characteristic curve analyses
Key Topics Covered
Methodology study describing score development and validation
The bHNDS is a new nutrient density score that aligns with the latest Dietary Guidelines for Americans and can be used to identify nutrient dense foods/beverages
Compared the performance of a new nutrient profiling model to two established models

Resiliency of the digestive system during aging and the impact of diet
Key Topics Covered
Narrative Review/White Paper
Comprehensive search of reviews
Explored physiological changes in digestive system with aging and impact of diet on these changes

Effect of oat β-glucan on affective and physical feeling states in healthy adults: Evidence for reduced headache, fatigue, anxiety and limb/joint pains
Key Topics Covered
Clinical Intervention Study
Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel arm design
Aimed to assess the effect of oat β-glucan on non-gastrointestinal symptoms in humans

In vitro–in vivo validation of stimulatory effect of oat ingredients on Lactobacilli
Key Topics Covered
Clinical Intervention Study
Oat products tested in vitro and a randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over human study
Explored oat ingredients effect on probiotics in the human gastrointestinal tract

A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials on the effects of oats and oat processing on postprandial blood glucose and insulin responses
Key Topics Covered
Systematic Review/Meta-Analysis
Review conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA)
Investigated effects of oats and oat processing on glycemic responses

The role of oat nutrients in the immune system: A narrative review
Key Topics Covered
Narrative Review
Discussed the relationship between oat nutrients and immune system response to infections

The effect of cereal β-glucan on body weight and adiposity: A review of efficacy and mechanism of action
Key Topics Covered
Systematic Review/Meta-Analysis
Four observational and 72 human intervention studies reviewed
Examined the relationship between β-glucan and body weight and adiposity

The prebiotic effects of oats on blood lipids, gut microbiota, and short-chain fatty acids in mildly hypercholesterolemic subjects compared with rice: A randomized, controlled trial
Key Topics Covered
Clinical Intervention Study
Randomized, controlled trial
Explored the effects of oat consumption on cholesterol and the gut microbiota

Increasing oat β-glucan viscosity in a breakfast meal slows gastric emptying and reduces glycemic and insulinemic responses but has no effect on appetite, food intake, or plasma ghrelin and PYY responses in healthy humans
Key Topics Covered
Clinical Intervention Study
Randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial
Aimed to determine the effect of β-glucan viscosity alteration on the primary endpoint of food intake

Impact of oat processing on glycemic and insulinemic responses in healthy humans: A randomized clinical trial
Key Topics Covered
Clinical Intervention Study
Randomized, crossover trial
Explored the effect of oat processing on glycemic and insulinemic responses
